Before any treatment, you should know the disease affecting your health. A disease can be infectious or non-infectious.
According to the mayo foundation, life-threatening diseases are infections from viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites.
It will help if you have basic medical education and a strong immune system to fight and prevent infection. Here is a vital information before you seek treatment.
What are Infectious Diseases?
Infectious diseases are illnesses that result from microbial attacks. These organisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. They may be harmless in themselves, but they trigger the development of infections. (1,2,3)
Infection refers to the entrance and development of an infectious agent in an animal body or human. (4)
Infectious diseases are contagious or communicable. In fact, most of them attack a wide range of animals besides humans. (2,5)
What are the top 3 infectious diseases?
Medically reviewed studies by the national health institute pose that the Big three infectious diseases are malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS. Moreover, tuberculosis is the most deadly of the three. (6,7)
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is an antiquity respiratory infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The infection records around 9-10 million new cases and 2 million deaths yearly. (8)
A 2019 peer-reviewed study poses that this infectious disease generally affects the lungs in 75% of patients, but it involves every organ. Individuals with HIV have an increased risk of contracting this infection. (9)
According to World Health Organization (WHO), approximately one-quarter of the world’s population is latently infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Malaria
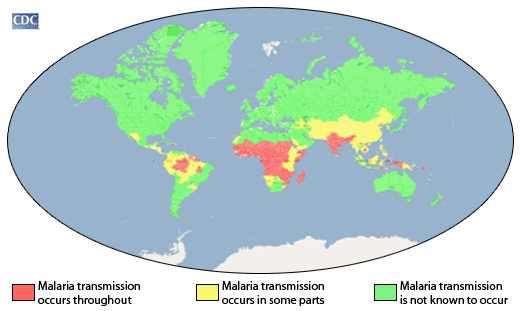
Malaria is a parasitic disease transmitted to humans through infected female Anopheles mosquito bites. (10)
It’s a life-threatening infectious disease that claimed the lives of 627,000 in 2020. The good news is that malaria is curable and treatable.
A 2021 Centers for disease control and prevention report showed that this infectious disease is very prominent in the poor tropical and subtropical areas of the world.
HIV/AIDS
The human immunodeficiency virus attacks the body’s immune system. If not treated, it leads to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. (11)
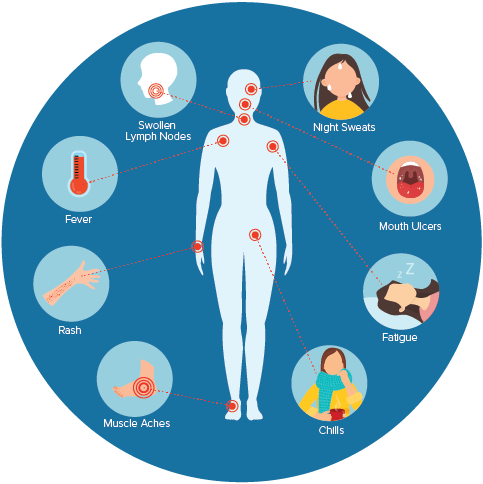
This infectious disease attacks the CD4 cells making the body susceptible to disease and infection. According to WHO, 37.7 million people were living with HIV at the end of 2020. (12)
Some symptoms, like flu, may emerge within 2-4 weeks after infection, but the most common signs are illustrated below.
What are clinical infections?
Clinical infection refers to a complete disease condition with a variety of symptoms. It often occurs after the disease has gone past the initial stages. (15)
For example, when you feel a headache, you may suspect malaria. Then, when you visit a doctor, a test is done, and it’s found that you have malaria.
Another factor is the subclinical infections where you don’t have the symptoms yet, meaning you don’t feel sick, but you choose to be screened, and a disease is found in your system.
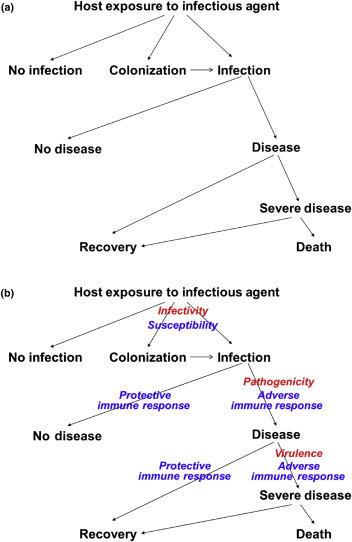
There are various outcomes when you get infectious diseases. Below is an illustration of the outcomes:
What is the clinical stage of infection?
The clinical-stage refers to the method used to determine the severity of a condition based on tests performed before applying treatments or surgery to carry out pathological stage tests.
These stages vary from one disease to the other. In fact, the WHO has four clinical staging systems for HIV/AIDS. (17)
What are the 4 types of infections?
Infections are categorized based on the microbial agent that causes them. The infectious diseases are caused by:
Viruses: are microscopic biological particles consisting of a genome, an external lipid envelope, and a protein capsid.
Most viruses are not curable, and the medical world use vaccines to control the spread of viral diseases. Examples are herpes zoster, common cold, and HIV/Aids. (18,19)
Fungi: These are eukaryotic organisms forming spores. A 2017 report poses that fungus causes 1.5million deaths and affects over a billion people globally.
The most common disease-causing fungi are Candida spp, which causes oral and genital thrush. (20)
Bacteria or (bacterial infections) are single-celled microorganisms that divide by binary fission. They lack a nuclear membrane. (21)
The bacteria that cause diseases are often Gram-negative groups. Most bacterial infections include strep throat or tonsillitis, Urinary tract infections, and tuberculosis. (22, 23)
Treatment for bacterial infection is through antibiotics.
Parasites: Parasites are organisms that simultaneously derive nourishment and injure the host. Most of the disease-causing parasites include Plasmodium, which causes malaria. (24)
What are the 4 stages of infectious diseases?
The clinical disease and transmission potentiality determines the stage of infection. (34)
These clinical stages vary from one disease to the other; some infections have all four, but others skip some stages. (35)
The most common stages of infectious disease include:
Stage 1: Incubation period
The incubation period is the duration from the first exposure to the infectious agent until the first signs or symptoms of a disease. In this stage, the disease is seldom found when a diagnosis is done. (36)
During this period, there is limited knowledge of the existence of the infectious agent in the body. (37)
Stage 2: Period of clinical illness
This is the period from the first appearance of symptoms to the last. It covers the time you start showing signs of infection to the last symptom. (38)
Stage 3: Latent period
The latent period is the time from exposure to an infectious agent to the onset of infectiousness. (39)
Stage 4: Period of communicability
This is the infectious period. It’s the time when an infected individual can transmit an infectious agent to others. (40)
What are 5 common infectious diseases?
There are several common infectious diseases globally. However, here are the top 5 according to the CDC and WHO reports.
A 2014 study by the national health institute found that there are 215 infectious diseases in the world.
CDC report of 2021 poses that 7.2 million healthcare visits occur each year due to infectious diseases.
However, top three infectious diseases are already discussed above but here are some more:
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) affects over 300 million people worldwide. It’s the prominent cause of liver disease and liver cancer. (41)
According to a medically reviewed study, viral hepatitis is transmitted through body fluids like semen, vaginal secretions, and blood. (42)
This infection has both acute and chronic disease clinical manifestations. In acute infection, patients have subclinical, icteric, or fulminant hepatitis. (43, 44)
However, in the chronic state, patients are in the symptomatic carrier stage with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis. (45)
Dengue
Dengue is also known as breakbone fever. Its symptoms include severe muscle spasms, dandy fever, and joint pain. (46,47)
Statistical evidence shows that dengue affects more than 100 million individuals annually and is the cause of up to 25 000 deaths worldwide. (48)
The disease is transmitted through Aedes mosquito bites carrying the DENV-1 to DENV-4). This infection is prominent in tropical and subtropical areas due to mosquitos’ infestations. (49,50)
Hepatitis C
A 2022 publication shows that viral hepatitis affects 185 million people worldwide.
Research shows that 80-85% of patients with hepatitis c who have acute infection often progress to the chronic infection stage. (51)
Effects of the chronic stage of viral hepatitis include portal hypertension, hepatic decompensation, and cirrhosis. (52)
Influenza
Influenza is a contagious flu viral disease affecting the upper respiratory tract. This infection shares a lot of symptoms with the common cold. (53)
It can be transmitted before the patient becomes symptomatic. However, it takes a few days for the patients to recover when the symptoms are not severe.
Nearly 10% of the world’s population is infected with these viruses yearly. (54)
Genital herpes
A 2016 research found that genital herpes affects 400 million people worldwide. It is a sexually transmitted disease caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV)
Hib disease
This infection is caused by bacteria that affect children younger than 5 years. It affects the central nervous system like the rabies virus.
What are the 7 types of infectious diseases?
Emerging infectious diseases
Emerging infectious diseases are illnesses that appear in a population for the first time or have been in existence but increase in geographic range and incidences. (25)
These infections include Lyme disease, West Nile virus, and SARS.
Sexually transmitted diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases are among the most common infectious diseases, especially in Africa. They consist mostly of bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Human papillomavirus is the most life-threatening sexually transmitted disease in the US.
These are infections that spread through sexual contact with an infected individual. Examples include genital herpes, vaginal candidiasis, and HIV/AIDS. (26)
Severe acute respiratory syndrome
A severe acute respiratory syndrome is a newly emerged viral infection from southern china. (27)
Studies pose that the origin of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus remains a mystery yet some data links its emergence to bats. (28)
Healthcare-associated infections
These are infectious diseases that occur while patients are receiving health care. They spread through contact with an infected person at the health facility.
The disease control and prevention center indicates that nearly 1.7 million cases of HCAIs are reported yearly, and 98,000 die from these infections. (29)
Zoonotic infectious diseases
According to the national institute of health, zoonotic infectious diseases are infections transmitted naturally from an infected animal to humans. (30)
Many infectious diseases originate from animals. In fact, more than 60% of human infections are zoonotic. (31)
Airborne diseases
These are primarily respiratory infections that spread through the air, i.e., the bacteria that causes whooping cough.
Foodborne infectious diseases
These infections spread through contaminated food or water, like infectious diarrhea. (32,33)
Respiratory syncytial virus
These are viruses that affect the breathing system. The respiratory syncytial virus is lethal in infants and older people.
What are the 10 examples of infectious diseases
- Whooping cough
- Pneumococcal disease
- Community-acquired pneumonia
- German measles
- Yellow fever
- Japanese Encephalitis
- Typhoid fever
- West Nile virus
- Herpes zoster
- Tetanus (the nervous system virus)
What are the 5 methods of disease transmission?
i) Indirect contact
a) Insect bites: like in the case of malaria and dengue infections. The carriers are insects, i.e., Lyme disease.
b) Food contamination: through consumption of contaminated food or water, you may get an infection.
ii) Direct contact
a) Animal to person: These are communicable infections from animals to humans through animal or insect bites.
b) Person to person: Infections spread from one person to another through contact or exchange of body fluids. i.e., German measles.
c) Mother to child: maybe an unborn baby or after birth through breastfeeding. Clinical trials suggest that some germs are transmitted from the mother to the baby at birth.
How to prevent infectious diseases
Its easier to prevent infections than seek for treatment. Follow these simple steps to keep safe from infection caused by lifestyle practices.
- Keep proper hygiene like hand washing and cleaning toilets.
- Consider staying at home when you are ill or feel sick.
- Avoid contact with animals which is the leading cause of zoonotic infections.
- Practice safe sex.
- Avoid sharing personal items to reduce risk factors.
- Wise travel to avoid infection outbreak zones.
- Maintain healthy immune systems with the 8 natural remedies.
Common symptoms of many infectious diseases
Many infectious diseases indicate similar symptoms. Below are some of the symptoms that may indicate an infectious disease attack.
- Coughing
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Diarrhea
When to see a doctor for infectious disease
Several infectious diseases, like cholera and Ebola, are extraordinarily lethal and may kill within a few hours. It would be best to seek diagnosis and proper ways of treatment.
- When you have a severe headache with a persistent fever
- Rushes or swollen part of the body
- Trouble breathing
- Muscle aches
- Animal bites
- Persistent cough and flu
- If you have other health or medical conditions
- History of an infectious disease
Summary
This article keeps you up to date with the reviews from national institutes concerning infectious diseases. Treatments for these diseases vary based on your immune system strength and severity.
In severe cases, treatment may include recommended vaccinations, especially in cases of viral infections. The information in this content should not override the advice of healthcare providers.

Pingback: 12 Home remedies for gout pain | GILEAD THERAPY
Pingback: 17 Home remedies for fungal infection | GILEAD THERAPY
Pingback: How to get rid of a cold sore:9 effective remedies | GILEAD THERAPY
Pingback: 7 Home Remedies for Cold flu | GILEAD THERAPY
Pingback: What are the factors causing disease? | GILEAD THERAPY